Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –
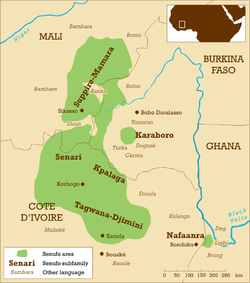
Nafaanra (sometimes written Nafaara, pronounced [nafãːra]), also known as Nafanan or Nafana, is a Senufo language spoken in northwest Ghana, along the border with Ivory Coast, east of Bondoukou. It is spoken by approximately 90,000 people. Its speakers call themselves Nafana, but others call them Banda or Mfantera. Like other Senufo languages, Nafaanra is a tonal language. It is somewhat of an outlier in the Senufo language group, with the geographically-closest relatives, the Southern Senufo Tagwana–Djimini languages, approximately 200 kilometres (120 mi) to the west, on the other side of Comoé National Park.
The basic word order is subject–object–verb, like Latin and Japanese. Like other Niger–Congo languages, it has a noun class system, with nouns classified according to five different classes, which also affects pronouns, adjectives and copulas. The phonology features a distinction between the length of vowels and whether they are oral or nasal (as in French or Portuguese). There are also three distinct tones, a feature shared with the other Senufo languages. Nafaanra grammar features both tense and aspect which are marked with particles. Numbers are mainly formed by adding cardinal numbers to the number 5 and by multiplying the numbers 10, 20 and 100. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that British communist leader Trevor Carter was the stage manager for the first British-Caribbean carnival, held in St Pancras Town Hall?
- ... that Lea Ackermann, a German nun of the Missionary Sisters of Our Lady of Africa, fought against forced prostitution and sex tourism in East Africa?
- ... that the Shady Rest Golf and Country Club was the home of John Shippen, the first African American to compete in the U.S. Open?
- ... that Malaysian businessman Lim Kok Wing was depicted as "King of Africa"?
- ... that Olive MacLeod journeyed 6,000 km (3,700 mi) through Africa in 1910–1911 to visit her murdered fiancé's grave, and wrote a book based on her observations?
- ... that the son of an engine fitter from England became Director of Education in part of modern-day South Africa for almost twenty years?
Categories
Selected biography –
Marcel Antoine Lihau or Ebua Libana la Molengo Lihau (29 September 1931 – 9 April 1999) was a Congolese jurist, law professor and politician who served as the inaugural First President of the Supreme Court of Justice of the Congo from 1968 until 1975, and was involved in the creation of two constitutions for the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Lihau attended the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium with the help of sympathetic Jesuit educators, becoming one of the first Congolese to study law. While there he encouraged Congolese politicians to form an alliance that allowed them to secure the independence of the Congo from Belgium. He served briefly as a justice official and negotiator for the Congolese central government before being appointed to lead a commission to draft a permanent national constitution. He was made dean of law faculty at Lovanium University in 1963. The following year he helped deliver the Luluabourg Constitution to the Congolese, which was adopted by referendum. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
|
| ||
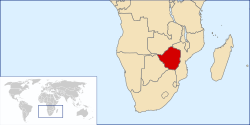
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It borders South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia to the northwest, and Mozambique to the east. The name Zimbabwe derives from "Zimba Remabwe" meaning "big house of stone" in the Shona language. Its use as the country's name is a tribute to Great Zimbabwe, site of the capital of the Empire of Great Zimbabwe. Zimbabwe's highest peak is Mount Nyangani, which lies within Nyanga National Park in the east of the country. The official language of Zimbabwe is English, however the majority of the population speaks Shona.
Under the leadership of former president Robert Mugabe and the current president Emmerson Mnangagwa, the economy of Zimbabwe declined from one of the strongest in Africa to one of the weakest and political tension has never been higher. In 1999, the Movement for Democratic Change was established and have campaigned for an end to "Mugabe's Reign of Terror". 80% of Zimbabweans are unemployed and inflation has soared to well over 15,000%. (Read more...)
Selected city –

Libreville (/ˈlɪbrəˌvɪl/; French: [libʁəvil]) is the capital and largest city of Gabon, located on the Gabon Estuary. Libreville occupies 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi) of the northwestern province of Estuaire. Libreville is also a port on the Gabon Estuary, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.
The area has been inhabited by the Mpongwe people since before the French acquired the land in 1839. It was later an American Christian mission, and a slave resettlement site, before becoming the chief port of the colony of French Equatorial Africa. By the time of Gabonese independence in 1960, the city was a trading post and minor administrative centre with a population of 32,000. Since 1960, Libreville has grown rapidly and now is home to one-third of the national population. (Full article...)
In the news
- 21 April 2025 – Spillover of the Sudanese civil war
- 2025 Nasir clashes
- The South Sudan People's Defence Forces capture the town of Nasir in Upper Nile State from the Nuer White Army. (Reuters)
- 19 April 2025 – Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria
- The death toll from clashes between cattle herders and farmers earlier this week in Benue State, central Nigeria, rises to 56. (Barron's)
- 19 April 2025 –
- A tavern owner is killed and four others are injured in a mass shooting during a live music performance at a tavern in Marble Hall, Limpopo, South Africa. No arrests were made. (SABC)
- 18 April 2025 –
- The death toll of the fire and capsizing of the wooden boat HB Kongolo on the Congo River in Democratic Republic of the Congo three days ago rises to 148. Hundreds of others remain missing. (Reuters)
- 17 April 2025 – Somali Civil War
- 2025 Shabelle offensive, American military intervention in Somalia
Updated: 17:05, 21 April 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ...that Iyabo Obasanjo-Bello, a Nigerian Senator from the People's Democratic Party, is the daughter of former President Olusegun Obasanjo?
- ...that the 2007 South Africa miners' strike, which impacted over 240,000 workers, was the first ever industry-wide miners' strike in the history of South Africa?
- ...that Seleh Leha, a town in Tigray Region in northern Ethiopia, was the site of a leprosarium built during the Italian occupation of East Africa and abandoned in 1941?
- ...that Sarir field, an oil field in Cyrenaica operated by the Arabian Gulf Oil Company (AGOCO), is considered to be the largest in Libya, with estimated oil reserves of 12 Gbbl (1.9×109 m3)?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus